Are you confused about PCI and PCIe? If you don’t know how to distinguish them, you can read this article which explains their differences in 4 aspects: functionality, appearance, speed and compatibility.
What is PCI and PCI Express?
In a computer, if different devices want to exchange data, they must do so over a certain channel (i.e., a bus). A bus is a universal communications backbone used to transfer information between the various functional components of a computer. It is a transmission harness composed of wires. PCI and PCIe are both buses.
What does PCI do in a PC?
PCI is the abbreviation of Peripheral Component Interconnect, which is the local bus in PC. So, how does it work in a computer?
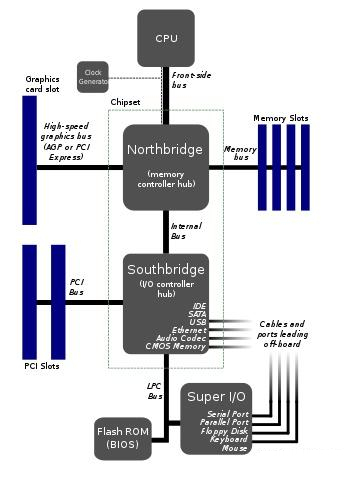
Years ago (around 2000-2010), the structure of a computer motherboard is as shown below.
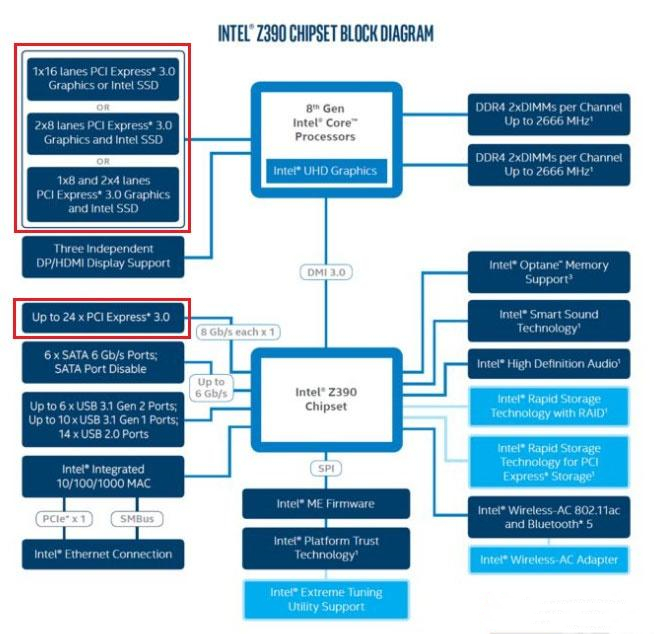
The picture above shows the structure of the new motherboard. In this motherboard, the Northbridge is fully integrated into the CPU, so there are only two main parts: the CPU and the Southbridge (hub or platform controller hub). Likewise, the graphics card and memory are connected directly to the CPU. But there are two points you should pay attention to: a. The graphics card is connected to the CPU through the PCIe bus; b. The motherboard supports a direct connection between the CPU and PCIe SSD. The chipset (Southbridge) is then connected to the CPU via the DMI (Direct Media Interface) 3.0 bus based on the PCIe bus. The Southbridge distributes 24 PCIe lanes for connecting hard drives, USB devices, network cards, sound cards, and more. It can be said that PCIe is more than just a local bus. It is already the system bus.
PCI and PCIe slots
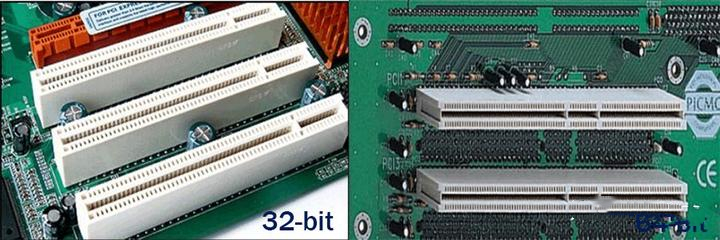
In this part, I'll show you what PCI and PCIe slots look like. PCI Slot: This slot comes in two types: 124-bit slot with 32 pins and 188-bit slot with 64 pins. The former is usually used for general desktop computers, and the latter is usually used for servers. The PCI slot is shown in the figure below:
PCIe: This slot comes in 7 versions: x1, x2, x4, x8, x12, x16 and x32, corresponding to 1/2/4/8/12/16/32 lanes respectively. Among them, PCI-E x32 has almost no corresponding mass-produced products due to its large size and is only used in some special occasions. PCI-E x12 is mainly used in servers and will not appear on consumer platforms. PCI-E x2 is primarily for internal interfaces, not expansion slots. Even though some motherboards offer this connector, PCI-E x2 basically comes in the form of an M.2 connector rather than a PCI-E slot.
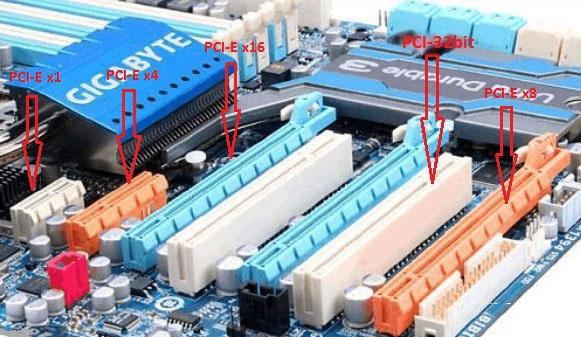
Therefore, the mainstream PCI-E slots on motherboards are basically concentrated in four types: PCI-E x1/x4/x8/x16. They are described in more detail below:
PCI-E x16 slot: It is 89 mm long and has 164 pins. It is typically used with graphics cards and is backwards compatible with x1/x4/x8 devices.
PCI-E x8 slot: It is 56 mm long and has 98 pins. It usually comes in the form of a PCI-E x16 slot, but only half of the data pins are active, meaning the actual bandwidth is only half that of a real PCI-E x16 slot. The purpose is to allow the graphics card with the PCI-E x16 interface to be successfully installed on the PCI-E x8 interface.
PCI-E x4 slot: It is 39 mm long and has 64 pins. It is mainly used to install PCI-E SSD or M.2 SSD (via PCI-E adapter). But in most cases, PCI-E x4 slots come from the factory as M.2 connectors.
PCI-E x1 slot: It is only 25 mm long and has 36 pins. The target products are relatively broad, including independent network cards, independent sound cards, USB 3.0/3.1 expansion cards, etc.
PCI-E x1/x4/x8/x16 slots are shown in the picture below:
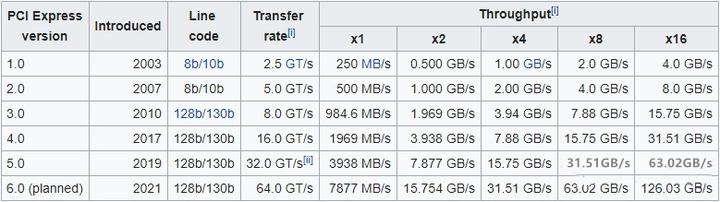
PCI vs PCIe speed
32-bit PCI speed is 133 MB/s, while 64-bit PCI speed is 266 MB/s. As for PCIe speed, it varies by channel and version, as shown in the table below:
Currently, most computers use PCIe version 3.0. With this version, even PCIe x1 can be much faster than 64-bit PCI. In terms of PCI vs PCI-E speed, PCI-E is the winner and it completely replaces PCI.
PCI and PCIe compatibility
PCI: 32-bit PCI interfaces are not compatible with 64-bit PCI products, while 64-bit PCI interfaces are compatible with 32-bit PCI products.
PCIe: PCI-E interfaces come in different lengths. The more lanes it has, the longer the interface. Generally, long slots are compatible with short interface products. For example, a PCIe X16 slot can be compatible with X4 or X8 products. But short slots are not compatible with long interface products because they cannot be inserted.
PCIe: PCIe comes in different versions. Different versions are compatible with each other. For example, PCIe 3.0 is compatible with PCIe 2.0. But the performance is determined by the lower version.
PCI vs PCIe: PCI-E interface and PCI interface are not compatible with each other.
PCI-E 1 to 4 PCI Express Port Riser Card
Send your message to us:
Post time: Nov-21-2023