Fast charging of mobile phones is divided into three major categories: VOOC flash charging fast charging technology, Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0 fast charging technology, MediaTek Pump Express Plus fast charging technology.
VOOC flash charging and charging for 5 minutes for 2 hours, charging for 30 minutes can charge the phone's power from 0% to 75%.
To achieve fast charging and charging functions on mobile phones, three elements must be met, and the three are indispensable. Charger, battery, charge IC. The charger needs to meet enough output current and output voltage because the charger's trace has a large parasitic resistance. If a larger charging current is to be achieved, the charger's on-load output voltage needs to be higher.
VOOC flash charge
VOOC flash charging and charging for 5 minutes for 2 hours, charging for 30 minutes can charge the phone's power from 0% to 75%.
There are two general directions for increasing the charging speed: one is to increase the voltage, and the other is to increase the current. Increasing the voltage will increase the amount of heat generated during the charging process, accelerate the aging of the battery and may pose a safety hazard, so the actual effect is not good. In contrast, increasing the current is more realistic.
VOOC flash charging technology uses a low voltage and high current mode to ensure safety during charging.
On February 23, 2016, Barcelona, Spain, OPPO presented its latest black technology at the 2016 Mobile World Congress (MWC 2016), which mainly includes the latest achievements in fast charging and imaging technology - OPPO VOOC super flash charging And SmartSensor image chip anti-shake technology, OPPO VOOC super flash charge for 15 minutes filled with a 2500 mAh mobile phone, charging 5 minutes for 10 hours.
Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0
Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0 technology is an upgraded version of Quick Charge 1.0 with new specifications. The charging speed is increased by simultaneously increasing the current and voltage.
MediaTek Pump Express Plus
MediaTek's fast charging technology, Pump Express, is built into the PMIC's power management IC. Allow the charger to determine the initial voltage required for charging according to the current. The pulse current command sent by the PMIC is transmitted to the charger through the USB Vbus. The charger adjusts the output voltage according to this command, and the voltage gradually increases up to 5V to reach the maximum charging current.
Comparison of high voltage fast charge and low voltage fast charge
As mentioned above, there are only three mainstream fast charging technologies: Qualcomm Quick Charge and MediaTek PEP high-voltage fast charging and VOOC flash charging low-voltage fast charging. All other fast charging technologies are in these three. Based on the modifications.
The advantage of high-voltage fast charging is that it does not need to make major modifications to the existing data lines and mobile phone batteries, and the cost is low, and the manufacturers using this technology are relatively more, the compatibility of the charger is better, and the disadvantage is that it has to go through two drops. Pressure, conversion loss is large, and the heat is severe during charging. Low-voltage fast charge currently only has VOOC flash charge. The biggest feature is low loss during charging. The previous charging speed is much faster than high-voltage charging. The disadvantage is that the compatibility is poor, and special accessories and mobile phone batteries are needed.
It is dangerous to charge a high-power mobile phone with a small power charger.
When the phone is charging, it is the phone itself that determines the charging current, not the charger. In general, the phone automatically detects the load capacity of the charger and determines the amount of current input based on its own power. For example, if you charge the 9V 1.67A Samsung S7 Edge with the Xiaomi 5V 1A charger, the charger will charge at the highest load. The charging current reaches 1.08A during the test. It is easy to heat and burn out after a long time. charger.
Therefore, you can use a high-power charger to charge a low-power mobile phone, but it is best not to use a low-power charger to charge a high-power mobile phone.
Why is fast charge more later more slow?
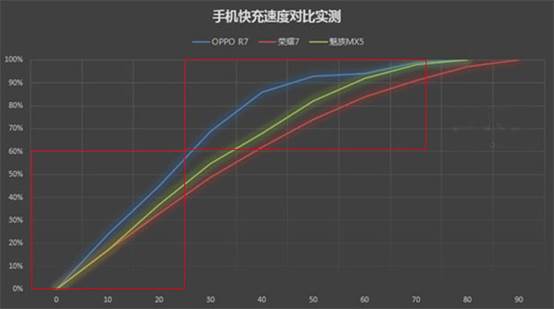
Many people may have discovered this problem: charging a low-power fast-charge mobile phone will be very fast at first, but after charging to a certain level, the charging speed will be slower and slower. For example, the fastest OPPO R7 uses less than 30 minutes from 0 to 60%, but it takes nearly 50 minutes from 60% to 100%.
This is actually normal. When the phone's power is very low, the phone will automatically drive the charger to fully replenish the battery. At this time, the charging speed is the fastest, but the heat and loss are also very large. After the battery is charged to 60%-80%, the general mobile phone will let the current drop and enter the stage of turbulent charge, which can reduce heat and protect the mobile phone hardware.
Relationship between Type-C interface and fast charge
USB Type-C is not just about changing the interface to a shape. A large part of it is to solve the problem of excessive current. Compared to the Micro USB interface, the USB Type-C has more contacts and can accommodate larger currents, naturally having the property of supporting fast charging.
If a mobile phone supports USB Type-C but does not support fast charging, its Typc-C is just a physical interface. To buy a USB Type-C interface, you must remember to buy a fast charging function and support charge fast Type-C power cable.
Send your message to us:
Post time: Mar-04-2019