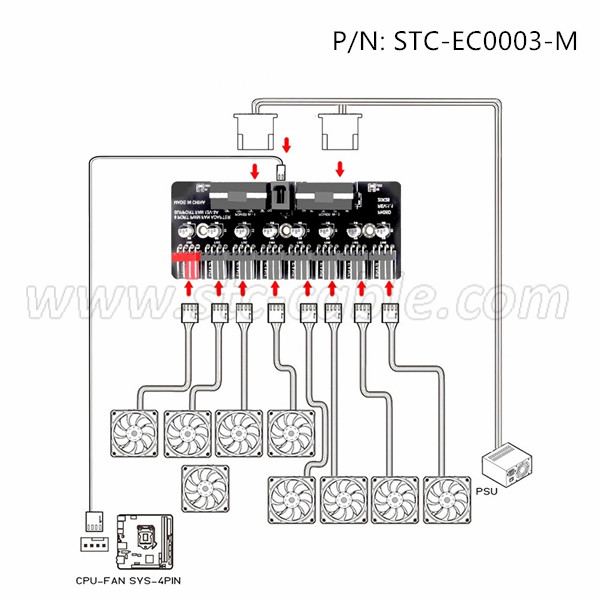
Principle of PWM intelligent temperature-controlled cooling fan
1. PWM technical background PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Intel has very strict evaluation standards for radiators.(10 Way PWM Fan Hub Splitter)
Traditional temperature-controlled fans use a temperature probe near the fan bearing to detect the temperature of the fan's air inlet, thereby adjusting the fan's speed. Although this kind of temperature control solves certain problems, it has rough accuracy, and the temperature control speed can only achieve high-speed and low-speed bipolar speed changes. PWM is the abbreviation of pulse width modulation circuit, which has been widely used in industrial control and microcontrollers. Intel combined it with the motherboard's CPU temperature detection and applied it to accurately control the speed of the radiator fan, and achieved good results.
2. Functional features of PWM intelligent temperature-controlled fans. First, the PWM fan adjusts the fan speed by obtaining temperature information directly from the CPU. There is no temperature measuring device on the fan.
The first, according to different CPU temperatures, the temperature-controlled fan will have different speed adjustments corresponding to it, and the fan speed can change to four levels, five levels, or even more, which is basically a feeling of infinite speed change. Due to the real-time adjustment of the pulse width signal, the fan speed changes very sensitively, and the changes in speed and CPU temperature are almost synchronized.
The second, the PWM fan can be kept at a very low speed when the computer is in standby mode. In standby mode, the CPU temperature is below 40 or 50 degrees Celsius, and its rotational speed is only about 1,000 rpm, which greatly reduces operating noise. The designed maximum speed, more than 2,000 rpm, will only appear when the CPU temperature is close to the extreme temperature, that is, 65-67 degrees. Compared with traditional temperature-controlled fans, it has a larger speed control range, which better solves the problems of noise and performance.
The third, when the PWM temperature-controlled fan is turned on, the speed will increase to the highest speed, and after a few seconds, it will drop to the low standby speed level.
These three characteristics are also the most obvious features of PWM smart temperature-controlled fans. (8 Way PWM Fan Hub Splitter) They can be used to determine whether the fan and motherboard really have PWM functions, or whether their functions are faulty. They can even be used as a reference for genuine and fake box radiators. Judgment criteria. 3. The simple principle of PWM intelligent temperature control fan. On the motherboard with PWM function, in addition to the original temperature measurement circuit, there is an additional PWM control chip. Its function is to send out a PWM control chip based on the CPU temperature measured by the temperature measurement circuit. PWM pulse signals with different duty cycles. This pulse is a square wave. Within a cycle, the high-level period of this square wave signal accounts for the proportion of the entire cycle, which we call the duty cycle. If the entire cycle is a high-level signal, the duty cycle is 100%, otherwise the duty cycle is zero. The simplest PWM temperature control circuit has an additional control circuit on the circuit board of the fan. We simply understand it as a triode, one of which is connected to the PWM square wave pulse. If a high level appears on this level, Then the other two poles of the triode are in the conducting state. If it is low level, the other two poles are in the disconnected state. If the duty cycle of the square wave pulse signal is 50%, that is, the high-level signal occupies half of a cycle, then the transistor will be in a conducting state for half of a cycle. Through the conduction time of this transistor in one cycle, we can easily control the fan speed. If the duty cycle of the PWM square wave pulse signal can be achieved at multiple levels, then the fan speed can also be achieved at multiple levels.
Send your message to us:
Post time: Oct-12-2023