What is the fastest growing power application today? There is no doubt that fast charging methods for mobile devices such as smartphones have a place. USB PD technology provides superior performance for fast charging of mobile devices, but at the same time it brings design and BOM cost challenges to power adapters. So what are the main challenges for power adapters for fast charging of mobile devices? How does the USB PD solution address these challenges?
In the future, power adapters will develop in the direction of smaller and smaller, higher power, faster charging speed and higher security. To meet these trends, the market needs IC solutions with high power density and ultra-high efficiency, and using fewer and smaller components, which requires USB PD solutions that can be optimized for AC/DC power supplies, which provide reliable , low-cost system solutions, and simplified adapter design.
What are the key challenges of fast charging?
Fast charging of mobile devices presents many challenges to power adapters, with cost, security and various fast charging protocols being the biggest challenges. There are many different fast charging protocols on the market, including Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0/3.0 (QC2.0/3.0), MediaTek PumpExpress Plus (PE+ 1.0/2.0), Samsung Adaptive Fast Charge (AFC), and Huawei Fast Charge Protocol. (FCP), Huawei Super Charge Protocol (SCP) for Direct Charge, other OEM proprietary protocols, USB Power Delivery (USB PD 2.0, 3.0), USB-IF Programmable Power Supply (PPS), Qualcomm Quick Charge 4+ ( QC4+) and so on. Other challenges include power density, constant voltage constant current (CVCC) specifications, efficiency, no-load standby power, dynamic load response, audible noise, user experience, and EMI / EMC common mode noise.
The ideal fast charging system is capable of negotiating any current and any voltage, regardless of the protocol, to overcome the various challenges of the power adapter system.
How to optimize AC/DC power supply?
USB PD provides more flexible power and data transfer over a single cable for maximum USB functionality. The power flow direction is no longer fixed. It optimizes power management across multiple peripherals and provides intelligent, flexible system-level power management. However, there are still some limitations in the AC/DC fast charging of mobile devices that need to be optimized.
Traditional USB PD solutions are not optimized for AC/DC power; some features are out of demand (eg, audio mode, bidirectional power flow). They are usually based on DSP or MCU, and their intrinsic controller ICs are costly. They require many external components and high system BOM costs, and require power hardware engineers to write software or firmware. The system design flow is often complex and the product design cycle is long. Therefore, the market needs a USB PD solution optimized for AC/DC.
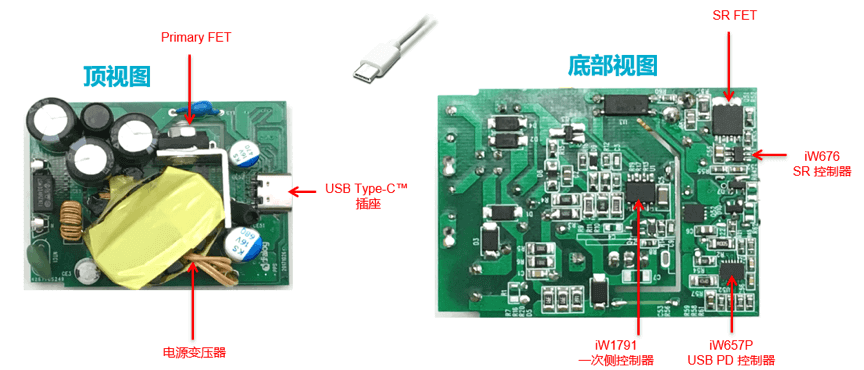
We introduce a USB PD solution, which is optimized for AC/DC, by iW1781 (primary controller optimized for USB PD), iW676 (synchronous rectification control optimized for direct charge and USB PD) And the iW656 (USB PD2.0 interface IC). In order to promote the evolution to USB PD 3.0 / PPS, Dialog also introduced the iW656P and iW657P secondary side interface IC. Both ICs support the USB PD 3.0 and PPS protocols and are combined with the primary side controller iW1791, which is an optimized USB PD 3.0 / PPS AC/DC solution.
How to simplify and optimize portable power adapters?
The key to simplifying and optimizing portable power adapters is the USB PD controller, which requires higher integration, covers a wider voltage range, and achieves lower IC costs.
The STC uses the iW657P USB PD controller, iW1791 main controller and iW676 SR controller in a USB PD / PPS power adapter design. Among them, iW656P / iW657P provides all the functions of iW656, and supports USB PD 3.0, Qualcomm QuickCharge 4+, USB PPS and direct charging. It offers VBUS resolution down to 10mV / step, onboard VBUS / TJ / VSD measurements and enhanced USB Type-C control, including VCONN support for smart cables. The iW657P also provides additional current sensing to measure secondary current through the onboard ADC and communicate with mobile devices for smarter control and protection.
Figure 1. USB PD/PPS Power Adapter Design Example Using iW657P + iW1791 + iW676
This is a single PCB board that implements a complete USB PD power adapter design that does not require a daughter board, whereas traditional solutions typically require a daughter board to host an MCU-based USB PD controller. This solution greatly simplifies the number of external components, enables simple power supply design, and eliminates the need to write software or firmware.
USB PD 3.0 is backward compatible with USB PD 2.0 and adds direct charging. It provides a new Enhanced Power Data Object (APDO) for programmable power modes. The mobile device can request and control the output voltage of the power adapter within a specified range with high precision and realize programmable current foldback. It provides a new mechanism to support direct charge and other charging algorithms. PPS requires 20mV / step voltage resolution and the minimum voltage can be reduced to 3.3V. The PPS-designed portable power adapter can directly charge the battery in the mobile device, including the smartphone, which helps solve the cooling and cost challenges of power management at the mobile device side.
Right Angle USB Type C Data and Charging Cord
Send your message to us:
Post time: Mar-22-2019