The main parameters of the hard disk
Buying a hard drive mainly depends on three parameters: hard drive type, interface type, storage capacity.
The type of hard disk depends on the use. For large-scale throughput calculations, solid-state is naturally required, because it has a very high transmission speed, and it only needs to use machinery for general storage. Needless to say, the storage capacity must be the higher the supported value, the better. If it is a mechanical hard disk, the capacity must be more than 1TB, and the solid-state hard disk should be determined according to the funds in hand. Next is the interface type. The hard disk is not as versatile as the monitor interface. Once the lower interface is selected incorrectly, it will really not work.
Hard disks are divided into mechanical hard disks (HDD), solid-state hard disks (SSD), and hybrid hard disks (SSHD) according to their structural principles.
According to the interface type, it is divided into: IDE, SATA, SCSI, SAS, PCIE, M.2, etc.
HDD
Hard disk drive, Hard Disk Drive (HDD), the most basic computer storage, HDD hard disk is also what we often call mechanical hard disk, mechanical hard disk is the working principle of traditional platter + magnetic head, data is stored on the platter, the magnetic head Compared with SSD solid state drives, the speed of HDD mechanical hard drives cannot keep up with the rhythm of technological innovation. The role of the current mechanical hard disk in the computer is basically only to store data files.
Hard drives can be divided into 3.5 inches, 2.5 inches, 1.8 inches, etc.
According to the number of revolutions, it can be divided into 5400rpm/7200rpm/10000rpm, etc. The higher the number of revolutions of the same type, the faster the speed.
According to the interface, it can be divided into IDE, SATA, SCSI, SAS, Fibre Channel hard disk, etc. ACHI is a soft interface technology, not a physical interface. Generally, ACHI is enabled by default on the SATA interface.
IDE
Electronic integrated drive interface, Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), commonly known as IDE interface, also known as parallel ATA interface, namely: parallel port (PATA, Parallel ATA). The English spelling of ATA is "Advanced Technology Attachment", which means "Advanced Technology Attachment". The ATA interface was first jointly developed by several companies such as Compaq and Western Digital in 1986, and was applied to desktop systems in the early 1990s. , due to its slow data transmission speed, too short cable length, few connected devices, no support for hot swapping, poor upgradeability of interface speed, etc., it has been eliminated.
SATA
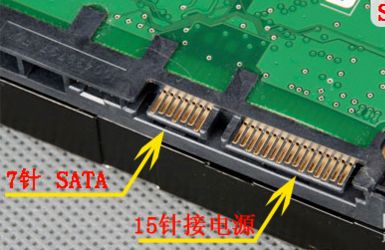
SATA is the abbreviation of Serial ATA, that is, serial ATA. SATA has completely replaced the old hard disk of the old PATA (Parallel ATA or formerly known as IDE) interface, and is named after the serial transmission of data. In terms of data transfer, SATA is faster than ever and supports hot swapping, allowing hardware to be plugged in or unplugged while the computer is running. On the other hand, the SATA bus uses an embedded clock frequency signal, which has a stronger error correction capability than before, and can check the transmission instructions (not only data), and automatically correct if errors are found, improving the reliability of data transmission.
SATA interface, there are 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 three versions, corresponding to SATA 1.5Gbit/s, SATA 3Gbit/s and SATA 6Gbit/s three specifications. There will be faster SATA Express specifications in the future.
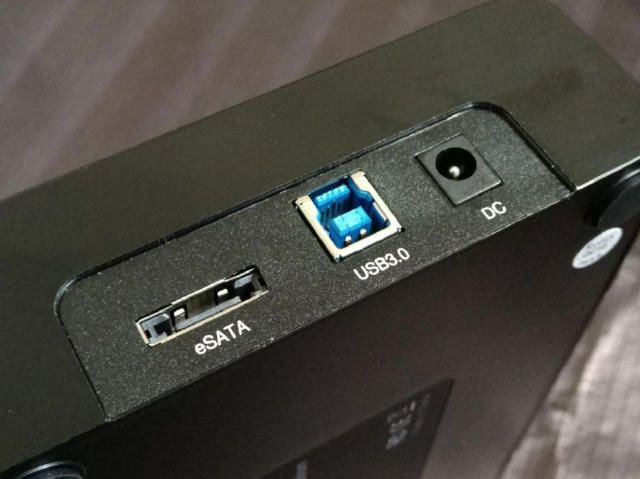
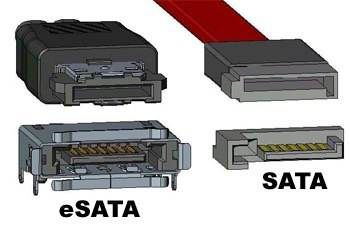
The SATA interface is generally used inside the chassis. In order to take advantage of the SATA hot-swap feature, an eSATA (External Serial ATA) interface used outside the chassis is derived. If your computer has an eSATA interface, you can easily connect the SATA hard drive to the chassis. eSATA interface connection without opening the case to replace the SATA hard drive. The eSATA interface and the USB interface are usually combined into one. At present, most of them still connect the hard disk with a conversion chip (hard disk box) and then use the usb interface to connect the external hard disk. Although this method is convenient, it will greatly reduce the transmission speed.
In addition, there is also the mSATA interface used on solid-state drives, which is mainly used in portable computers: such as business notebooks, ultrabooks, mainstream notebooks, etc.
SCSI
Small computer system interface (Small Computer System Interface, SCSI) is a parallel port, but it is completely different from IDE (ATA). IDE interface is the standard interface of ordinary PC, while SCSI is not an interface specially designed for hard disks. It is widely used in High-speed data transfer on minicomputers, servers.
SAS
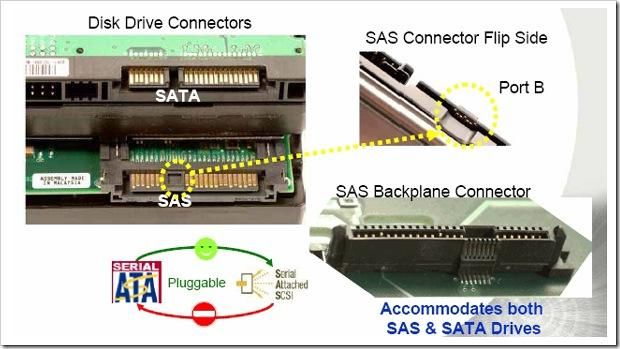
Serial Attached SCSI interface (Serial Attached SCSI, SAS), SAS is a new generation of SCSI technology, and the same as the popular Serial ATA (SATA) hard disk, both use serial technology to obtain higher transmission speed, and shorten the Links improve interior space, etc. SAS is a new interface developed after the parallel SCSI interface. This interface is designed to improve the performance, usability and expandability of storage systems, and to provide compatibility with SATA hard drives. The SAS interface not only looks similar to SATA, but is also backward compatible with the SATA standard. That is, the backpanel of the SAS system can be connected to both high-performance SAS drives with dual ports and high-capacity, low-cost SATA drives. As a result, SAS drives and SATA drives can exist in one storage system at the same time. It should be noted, however, that SATA systems are not SAS compatible, so SAS drives cannot be connected to the SATA backplane. Due to the compatibility of SAS systems, IT personnel can use hard drives with different interfaces to meet the capacity or performance requirements of various applications, so they have more flexibility when expanding storage systems, allowing storage devices to maximize investment benefits.
SSD
Solid State Drive, Solid State Disk or Solid State Drive (SSD), commonly known as solid state drive, solid state drive is a hard drive made of solid-state electronic storage chip arrays, named because solid capacitors are called Solid in Taiwanese English. SSD consists of control unit and storage unit (FLASH chip, DRAM chip). The data reading speed of solid-state drives is very fast, which is why many people add solid-state drives to their computers.
There are two types of storage media for solid-state drives, one is to use flash memory (FLASH chip) as the storage medium, and the other is to use DRAM as the storage medium.
According to the appearance, there are two versions of solid-state drives, one is the SATA interface version and the other is the M.2 interface version. The first is the SATA interface, which is inherited from the traditional mechanical hard disk and is the most mainstream hard disk interface form. Due to its long existence, the SATA interface is extremely compatible. Almost all types of motherboards have SATA interfaces. It is the most popular hard disk interface on the market. In terms of performance standards, the SATA interface of solid-state drives on the market generally adopts the SATA III standard, and the theoretical maximum speed is 6Gbps. The read performance of most SSDs based on SATA interface will normally be above 500MB/S.
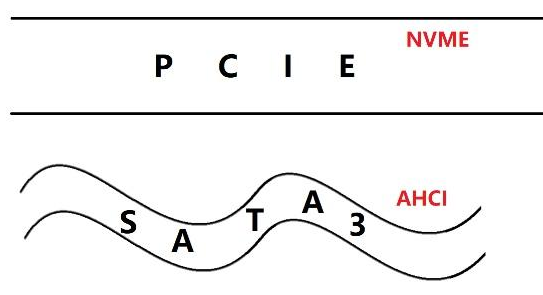
As for the M.2 interface, it is actually a new interface specially prepared for solid-state drives. The card slot of the M.2 interface generally has the size of 2280/2260, and the mainstream M.2 interface solid-state size is basically the size of 2280. The M.2 interface is essentially a PCIe slot. PCIe is a high-speed channel. Different SSD transmission protocols will affect the transmission performance. It supports the NVMe protocol. The M.2 interface that uses the PCIe channel will be better than the M.2 interface that does not use PCIe quick.
If you want to improve the performance of old platforms, such as Intel 4th generation, some motherboards have no M.2 interface at all, then SATA SSD is enough. If the motherboard is a newer platform, such as the Ryzen 2nd generation, Intel 8th generation platform, or M.2 SSD, the speed improvement is still obvious. If you are a high-end user, used to design rendering, large-scale games, don't hesitate! M.2 NVMe SSD is required, and data transfer is fast enough to meet high-end platforms.
FLASH
Flash-based solid-state drives (IDEFLASH DISK, Serial ATA Flash Disk): FLASH chips are used as storage media, which is also commonly referred to as SSD. Its appearance can be made into a variety of styles, such as: notebook hard disk, micro hard disk, memory card, U disk and other styles. The biggest advantage of this kind of SSD solid state drive is that it can be moved, and data protection is not controlled by power supply, it can adapt to various environments, and is suitable for individual users. Generally, the number of erasing and writing is about 3000 times. Take the commonly used 64G as an example. Under the balanced writing mechanism of SSD, the total amount of data that can be erased and written is 64G X 3000 = 192000G. If you are a perverted video king who likes to download every day If you download 100G every day after watching the video, the number of days available is 192000 / 100 = 1920, which is 1920 / 366 = 5.25 years. If you are just an ordinary user who writes data far less than 10G per day, take 10G as the calculation, you can use it continuously for 52.5 years, and if you use a 128G SSD, you can use it continuously for 104 years! What is this concept? Like ordinary hard disk HDD, it can theoretically read and write infinitely.
DRAM
DRAM-based solid-state drives: DRAM is used as a storage medium and has a narrow range of applications. It imitates the design of traditional hard disks, and can be used for volume setting and management by file system tools of most operating systems, and provides industry-standard PCI and FC interfaces for connecting to a host or server. Application methods can be divided into two types: SSD hard disk and SSD hard disk array. It is a high-performance memory and has a long lifespan, the fly in the ointment is the need for an independent power supply to keep data safe. DRAM SSDs are relatively non-mainstream devices.
M.2
The M.2 interface is a new host interface scheme that is compatible with a variety of communication protocols, such as sata, PCIe, USB, HSIC, UART, SMBus, etc. The M.2 interface is a new-generation interface standard tailored for Ultrabooks to replace the original mSATA interface. Whether it is a smaller size or higher transmission performance, M.2 is far superior to mSATA.
There are two types of M.2 interfaces: Socket 2 (B key, NGFF) and Socket 3 (M key, NVME). Among them, Socket 2 supports SATA and PCI-E X2 interfaces, and if the PCI-E ×2 interface standard is used, the maximum The read speed can reach 700MB/s, and the write speed can also reach 550MB/s. Among them, Socket 3 can support PCI-E × 4 interface, and the theoretical bandwidth can reach 4GB/s.
The channels supported by the M.2 interface of different motherboards are different, and some only support the PCI-E channel, which is indicated in the description of M.2 in the specification. Some are compatible with both SATA and PCI-E channels. So if you want to buy an M.2 SSD, you must first know which channel the M.2 interface on your motherboard supports. The hard disk master control determines whether the SSD connected to the M.2 interface uses the PCI-E channel or the SATA channel. For example, the master controller of HyperXPredatorSSD is Marvell88SS9293 master controller.
The paths are different, and the speed is naturally different. The theoretical bandwidth of SATA3.0 channel is 6Gb/s. The theoretical limit transfer speed is 600MB/s, so like all SATA interface SSDs on the market, the maximum read speed of Kingston G2 series M.22280SSD does not exceed 600MB/s, while the motherboard M. .2 The interface takes the PCI-E channel and the transmission channel bandwidth is 10Gb/s. The sequential read and write of HyperXPredatorSSD reaches 1400MB/s and 1000MB/s, completely exceeding the limit transfer speed of SATA3.0.
Under the M.2 interface, PCI-E and SATA3 are simply the "road" for data. PCI-E is like a very wide road, and data can travel very fast, while SATA3 is more like a road. On rough roads, the data travels very slowly, but the CPU is so big inside, and there are not many roads to be repaired, so there are only a few PCI-E channels. The last thing I want to talk about is NVMe, which is often used as a selling point by merchants. In fact, NVMe and AHCI are both a norm. It is like walking on the road. If there are no traffic rules, then it must be crowded. Moved, and NVMe and AHCI are like this kind of traffic rules.
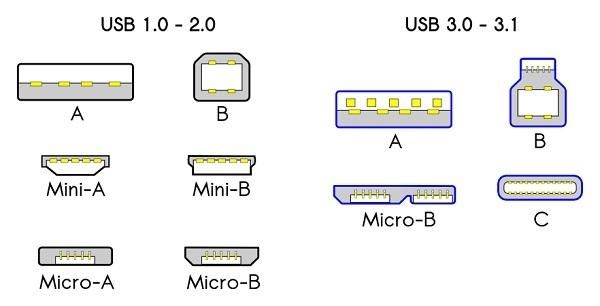
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an external bus standard used to standardize the connection and communication between computers and external devices, and is mainly used for mobile storage devices (mobile hard disks, U disks, etc.)
Main USB standards: USB1.1, supporting 1.5Mbps at HalfSpeed and 12Mbps at FullSpeed; USB2.0, supporting 480Mbps at High Speed; USB3.0, supporting SuperSpeed ) of 5Gbps. USB 2.0 is based on a half-duplex two-wire bus, which can only provide unidirectional data flow transmission. USB 3.0 uses dual simplex four-wire differential signal lines, so it supports bidirectional concurrent data streaming.
The USB3.0 mobile hard disk connected to the eSATA interface will be faster than the USB2.0 interface, but it will be slower than the one directly plugged into the USB3.0 interface. The maximum transfer speed of the USB3.0 interface can reach 500MB/s, the maximum transfer rate of the eSATA interface cannot exceed 300MB/s, and the maximum transfer speed of the USB2.0 interface is only 60MB/s, so if the computer has an eSATA interface or USB3.0 interface, USB3.0 is the first choice for mobile hard disk, and its transmission speed will be much higher than USB2.0.
In order to adapt to changeable devices, the usb interface has derived standard USB, mini USB, micro USB, USB Type-C and other interfaces. In addition, we often see two interfaces connected side by side on mobile hard drives, which are also USB A variant of the interface.
SSHD
Hybrid solid state drive (Solid State Hybrid drive, SSHD), to put it bluntly, is HDD+SSD=SSHD. The main body of the SSHD hard disk is a mechanical hard disk, but the disk body comes with a flash memory module. This flash memory module is responsible for data processing and data processing. We can also understand the flash memory module equipped on this hybrid hard drive as an SSD solid state drive, but the capacity of this SSD solid state drive is not large. Generally, the SSD in the hybrid hard drive is used to start the operating system, and the SSD module in the hybrid hard drive is used. It is the storage system cache file.
Send your message to us:
Post time: Aug-05-2022
.jpg)